Parameter documentation
PyHIST usage: pyhist.py [arguments] input_image
PyHIST parameters
- Positional: input image
- Optional: show PyHIST's help message.
- Execution: controls how the tile extraction should be performed.
- General output: controls what outputs to save.
- Downsampling: control the WSI resolutions to use during PyHIST's execution.
- Random sampling: parameters applicable to the random sampling method only.
- Graph segmentation: parameters applicable to the graph-based segmentation method only.
Graph-based segmentation parameter tuning examples
PyHIST parameters
Positional
Input image
input_image
The whole slide image input file.
Optional
Help
-h, --help
Print the help page and exit.
Execution
Controls how the tile extraction should be performed. These parameters are applicable to any tile extraction method in PyHIST.
Patch size
--patch-size
Integer indicating the size of the produced tiles. A value of P will produce tiles of size P x P. (default: 512).
Tile generation method
--method {randomsampling,graph,graphtestmode,otsu,adaptive}
Method to perform the segmentation. (default: graph)
Format
--format {png,jpg}
Format to save the tiles. (default: png)
Content threshold
--content-threshold CONTENT_THRESHOLD
Threshold parameter indicating the proportion of the tile area that should be foreground (tissue content) in order to be selected. It should range between 0 and 1. Not applicable for random sampling. (default: 0.5)
Pipeline execution information
--info {silent,default,verbose}
Show status messages at each step of the pipeline (default: default).
General output
Controls what outputs to save as the result of PyHIST's execution. Note that by default, PyHIST won't save any output. This is to prevent an unintended generation of large amounts of files. Output saving must be enabled explicitly.
Output
--output OUTPUT
Output directory (default: output/)
Save patches
--save-patches
Save the tiles with an amount of foreground above the content threshold. (default: False). (default: False)
Save blank
--save-blank
If enabled, background tiles will be saved (i.e. those that did not meet the content threshold.). (default: False)
Save non-square
--save-nonsquare
By default, only square tiles are saved, discarding the regions towards the edges of the WSI that do not fit a complete tile. If this flag is enabled, these non-square tiles will be saved as well. (default: False)
Save tilecrossed image
--save-tilecrossed-image
Produce a thumbnail of the original image, in which the selected tiles are marked with a blue cross. (default: False)
Save mask
--save-mask
Keep the mask used to perform tile selection. (default: False)
Downsampling
These parameters control the WSI resolutions to use during PyHIST's execution.
Output image downsampling
--output-downsample OUTPUT_DOWNSAMPLE
Downsampling factor for the output image. Must be a power of 2. (default: 16)
Mask downsampling
--mask-downsample MASK_DOWNSAMPLE
Downsampling factor to calculate the image mask. A higher number will speed up the tiling evaluation process at the expense of tile evaluation quality. Must be a power of 2. (default: 16)
Tilecrossed image downsample
--tilecross-downsample TILECROSS_DOWNSAMPLE
Downsampling factor to generate the tilecrossed overview image. Must be a power of 2. (default: 16)
Test image downsample
--test-downsample TEST_DOWNSAMPLE
Downsampling factor to generate the test image in graph test mode. Must be a power of 2. (default: 16)
Random sampling
Parameters applicable to the random sampling method only.
Number of tiles to sample
--npatches NPATCHES
Number of tiles to extract in random sampling mode
Graph segmentation
Parameters applicable to the graph-based segmentation method only.
Save Canny edge image
--save-edges
Keep the image produced by the Canny edge detector. (default: False)
Borders
--borders {1000,1111,1010,1100,0111,1011,1101,1001,0011,0100,0001,0101,0110,1110,0000,0010}
A four digit string. Each digit represents a border of the image in the following order: left, bottom, right, top. If the digit is 1, then the corresponding border will be taken into account to define background. For instance, with 1010 the algorithm will look at the left and right borders of the segmented image, in a window of width defined by the --percentage-bc argument, and every segment identified will be set as background. This argument is mutually exclusive with --corners. If --borders is set to be different from 0000, then --corners must be 0000. (default: 1111)
Corners
--corners {1000,1111,1010,1100,0111,1011,1101,1001,0011,0100,0001,0101,0110,1110,0000,0010}
A four digit string. Each digit represents a corner of the image in the following order: top left, bottom left, bottom right, top right. If the digit is equal to 1, then the corresponding corner will be taken into account to define background. For instance, with 0101, the bottom left and top right corners of the segmented image will be considered, with a square window of size given by the --percentage-bc argument, and every segment identified will be set as background. This argument is mutually exclusive with --borders. If --corners is set to be different from 0000, then --borders must be 0000. (default: 10000)
K-const (segmentation granularity)
--k-const K_CONST
Parameter used by the segmentation algorithm to threshold regions in the image. This value controls the degree to which the difference between two segments must be greater than their internal differences in order for them not to be merged. Lower values result in finer region segmentation, while higher values are better to detect large chunks of tissue. Larger images require higher values. (default: 10000)
Minimum segmentsize
--minimum_segmentsize MINIMUM_SEGMENTSIZE
Parameter required by the segmentation algorithm. Minimum segment size enforced by post-processing. (default: 10000)
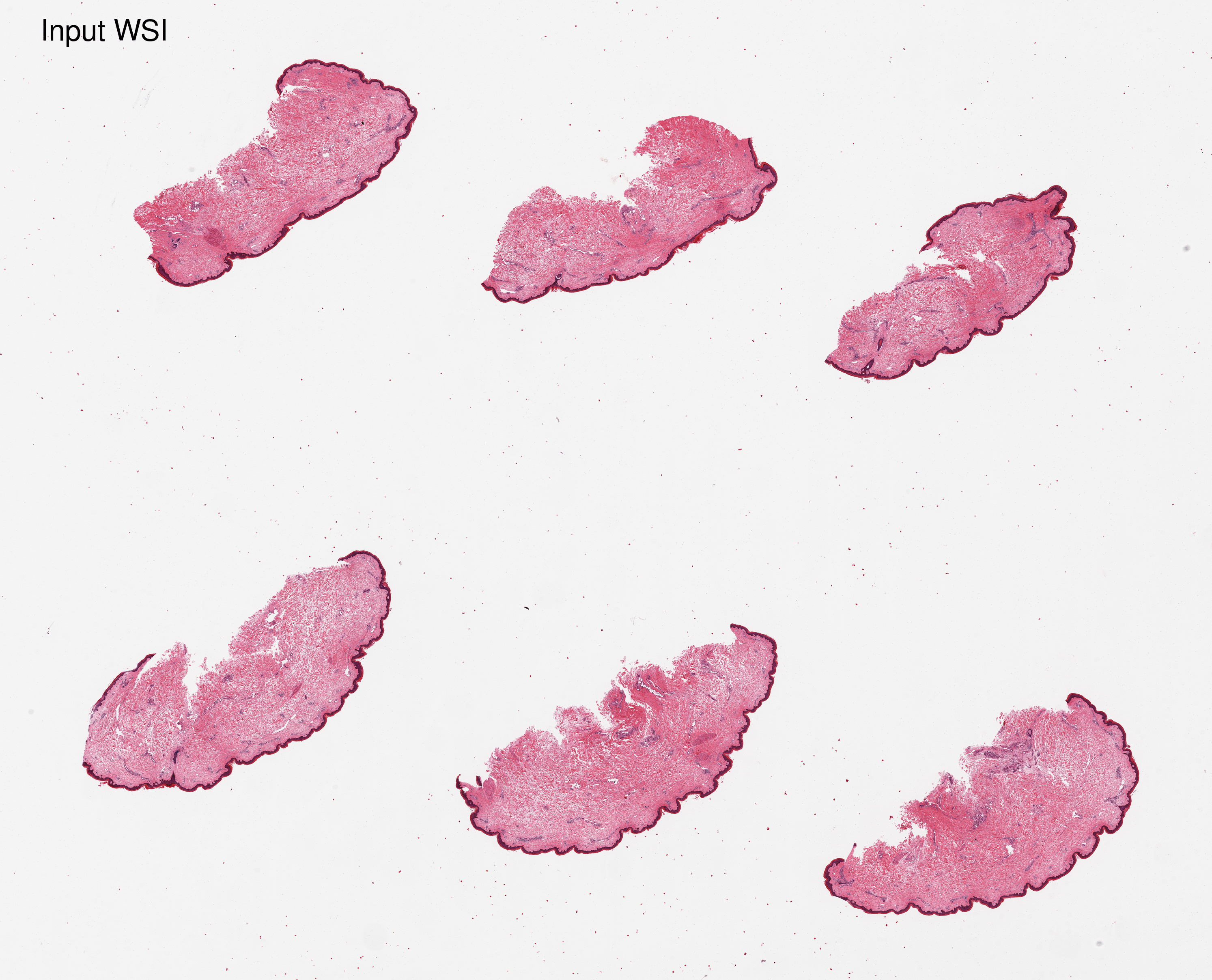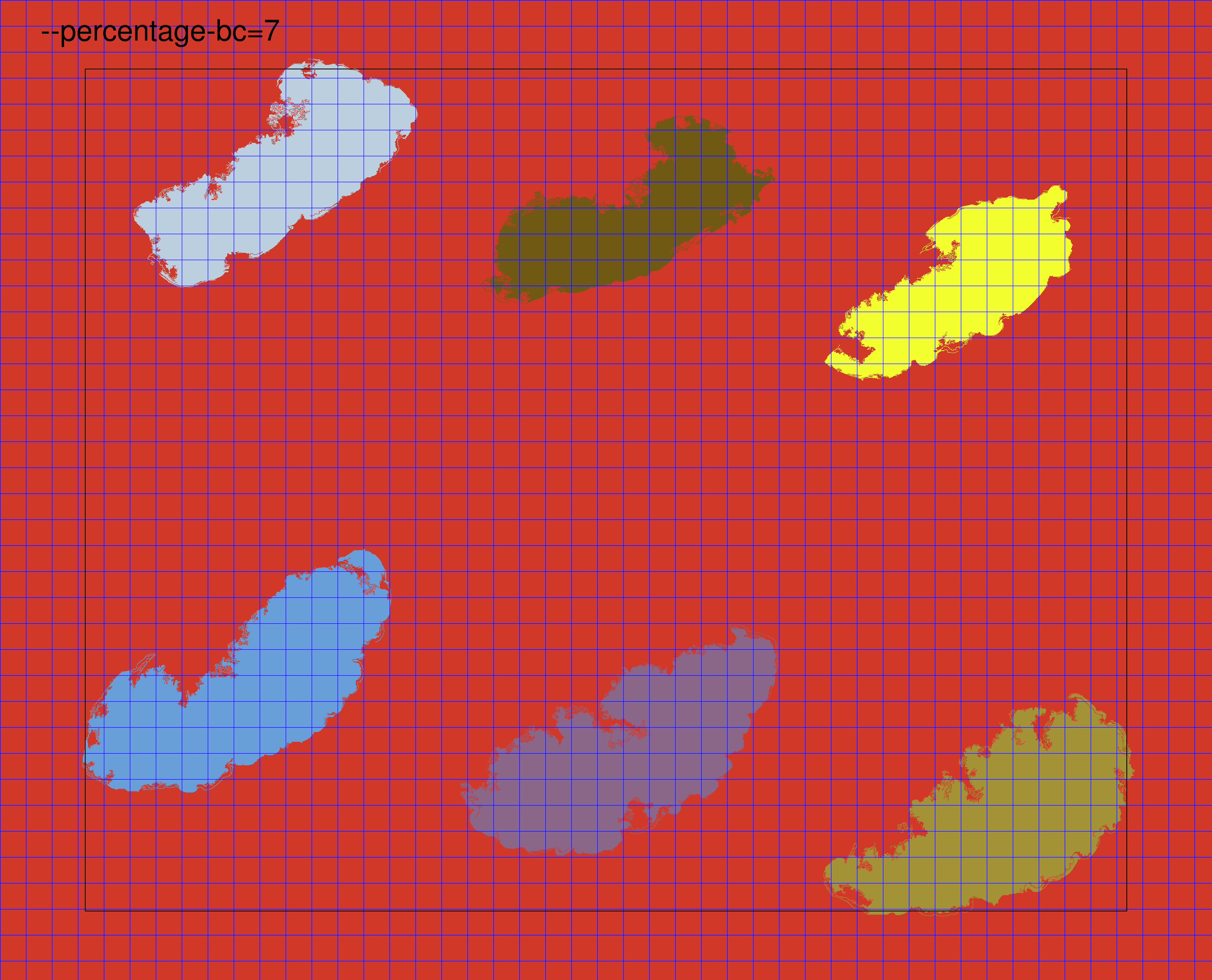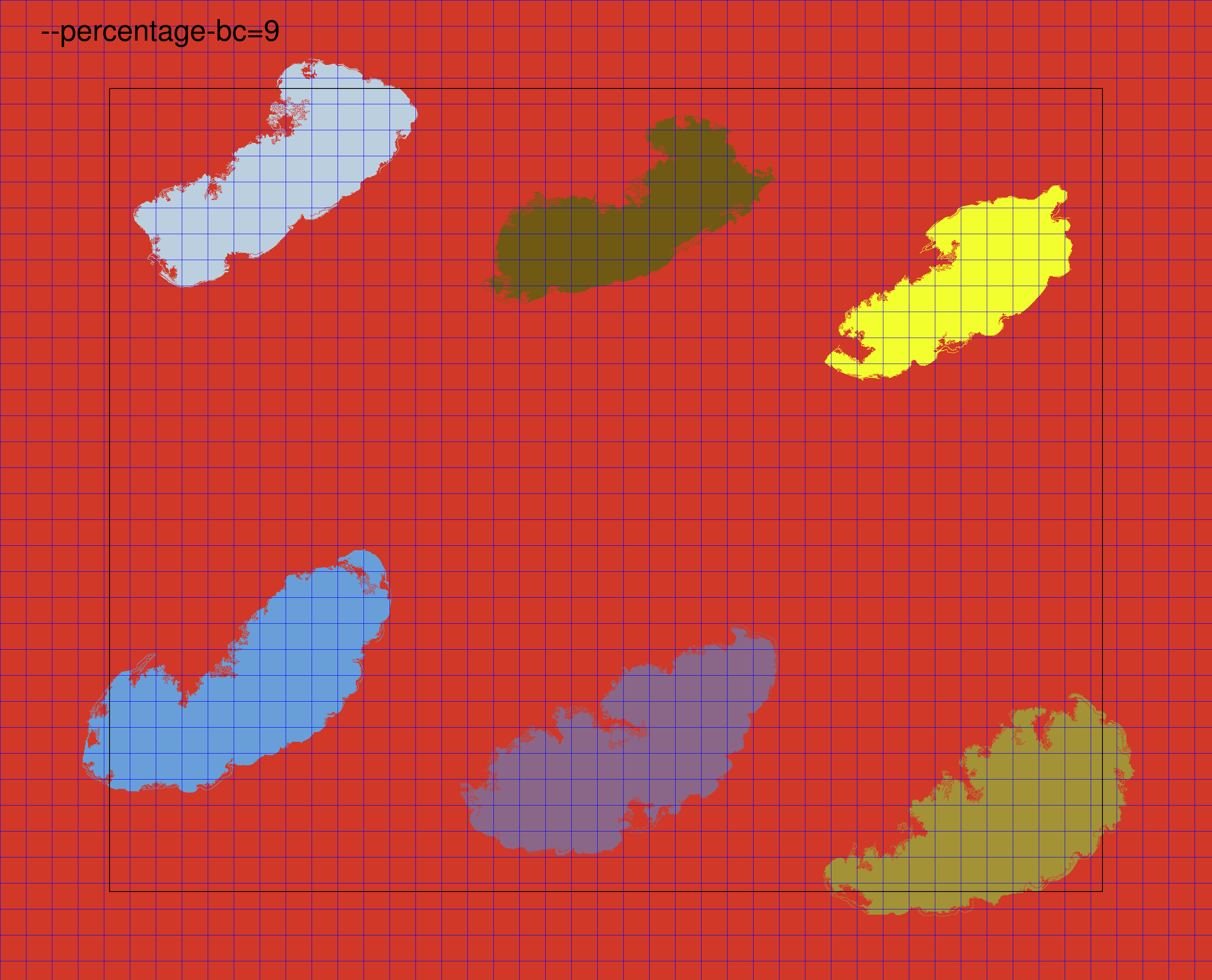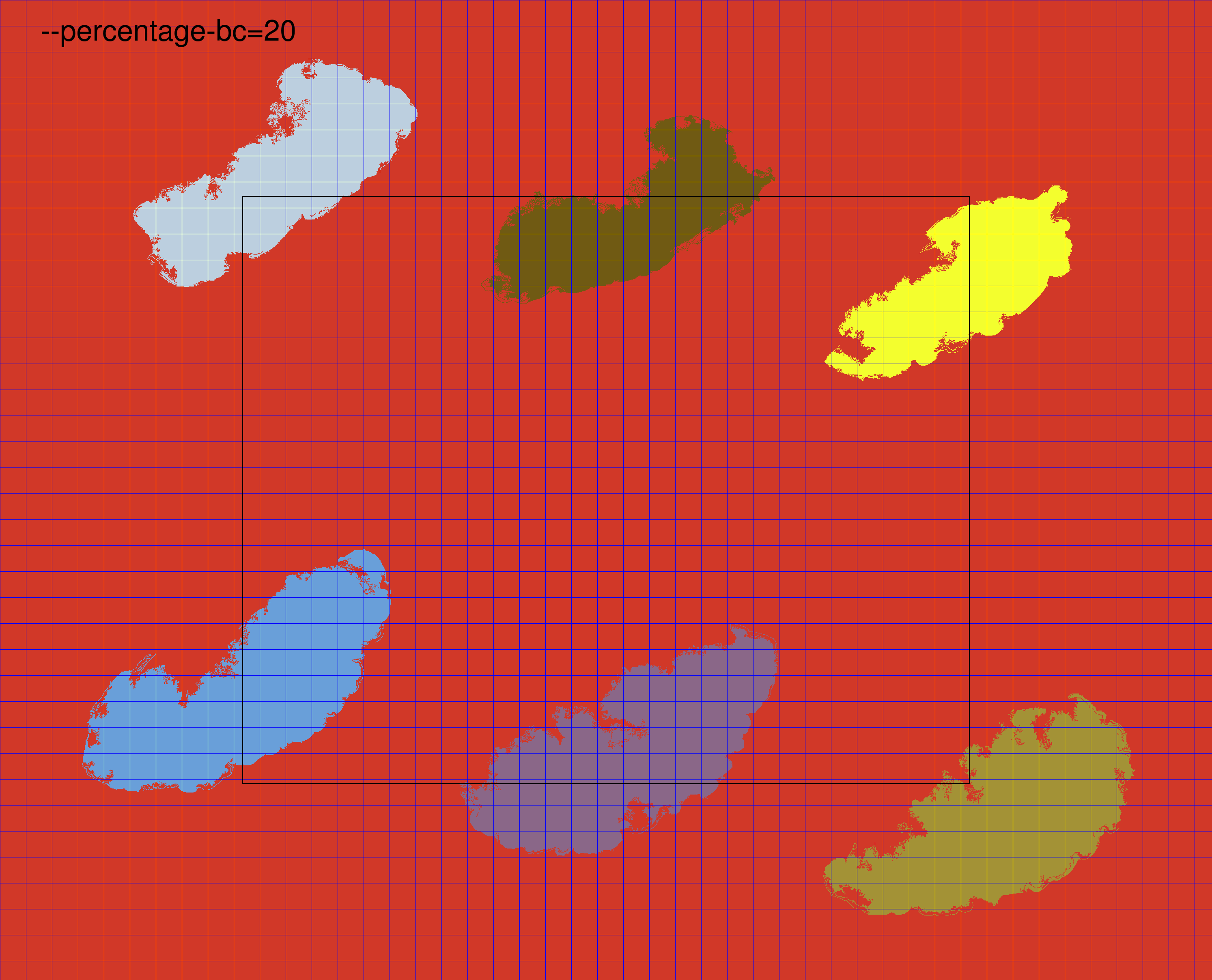
Borders and corners background percentage
--percentage-bc PERCENTAGE_BC
Integer [0-100] indicating the percentage of the image (width and height) that will be considered as border/corner in order to define the background. (default: 5)
Sigma
--sigma SIGMA
Parameter required by the segmentation algorithm. Used to smooth the input image with a Gaussian kernel before segmenting it. (default: 0.5)
Graph-based segmentation parameter tuning examples
K-const
The k constant is used by the graph segmentation algorithm to set a scale of observation. Setting a high value of k will lead to the algorithm detecting segments of a large size, while lowering it will result in a finer region segmentation. Here, we show an animated example of increasing the value of --k-const up to the default of 10000. As the value increases, the regions detected as a single unit are larger. Further details on the specific meaning of this parameter are available in the graph segmentation method paper. We find that the default value of k tends to work well for many types of WSIs.
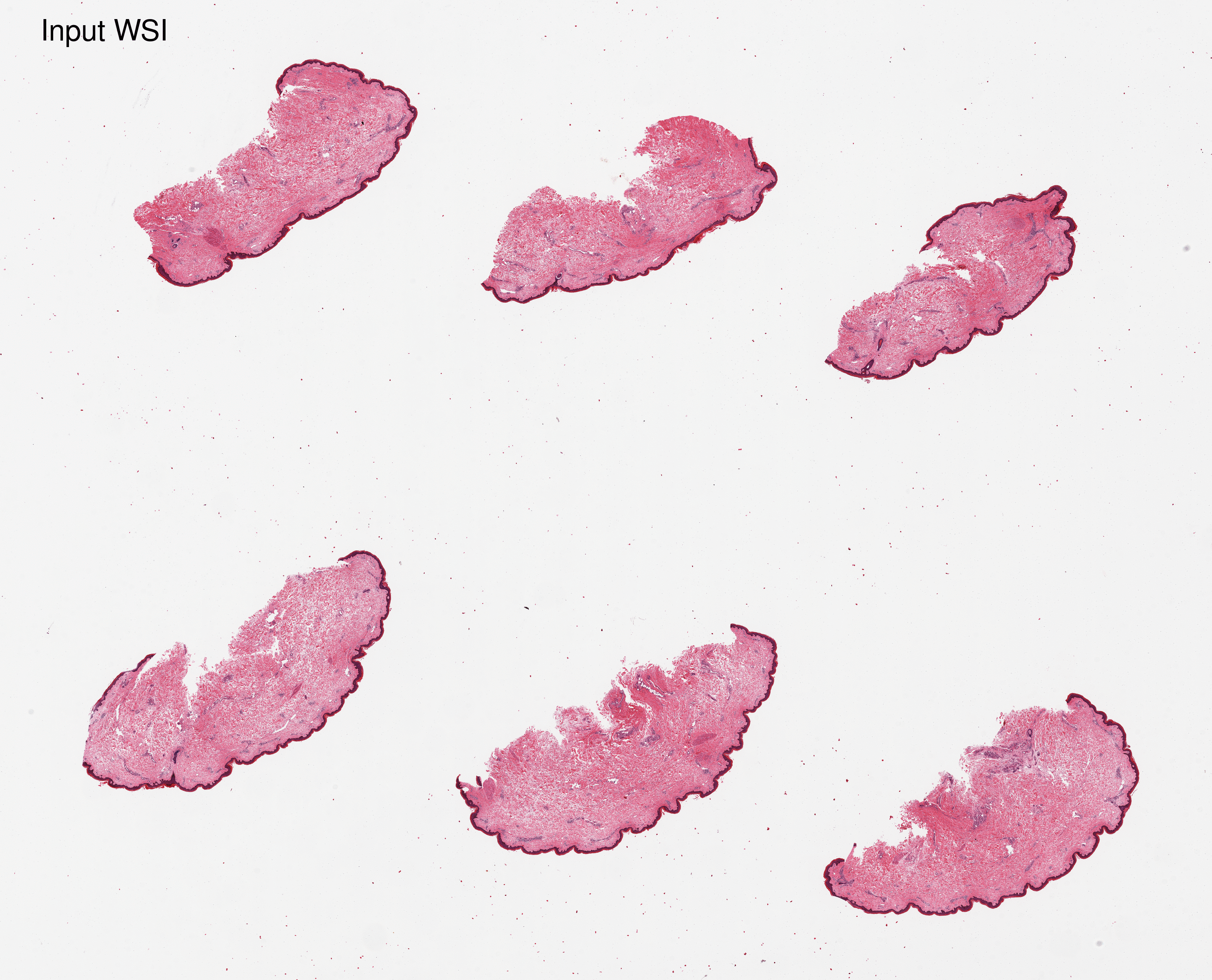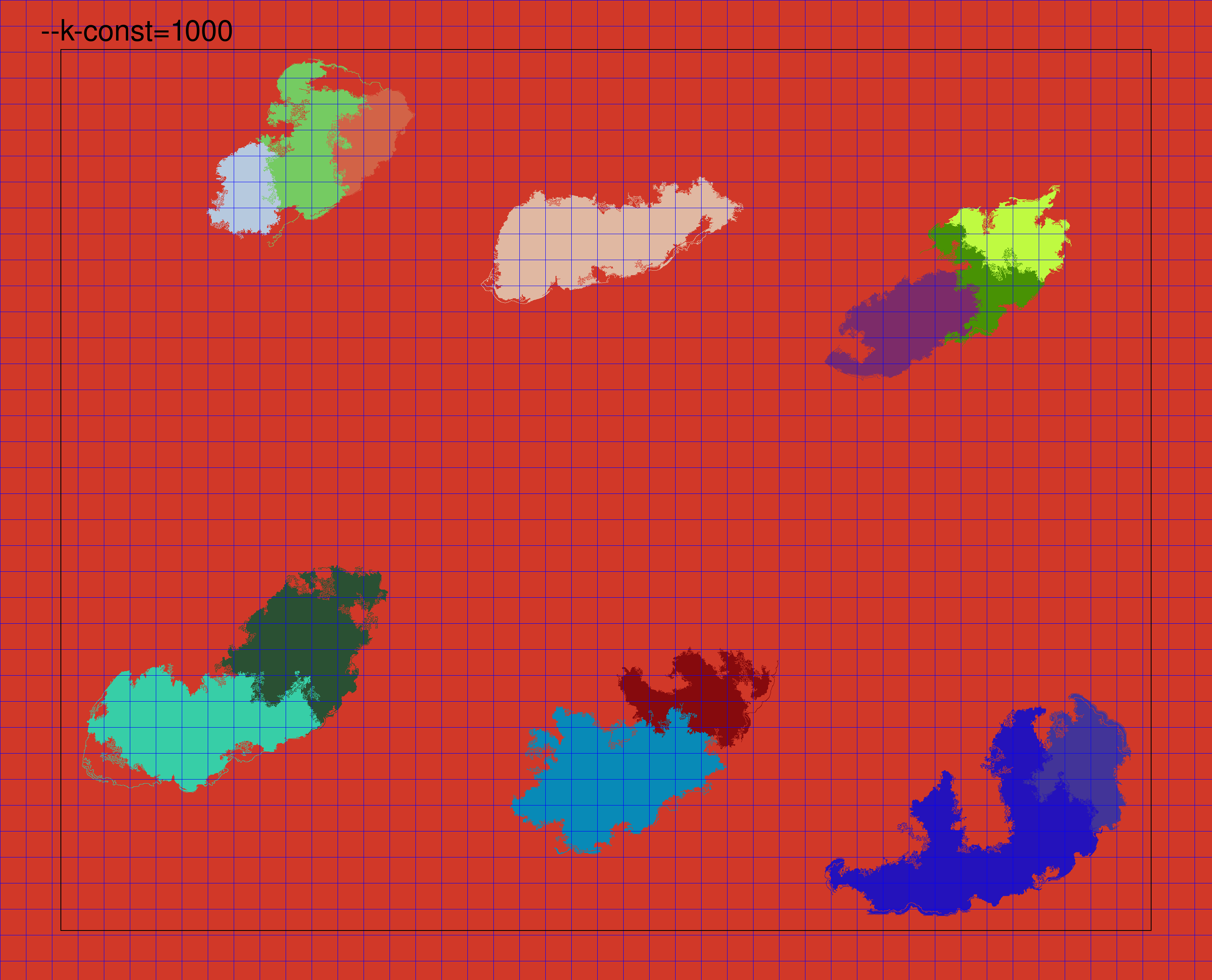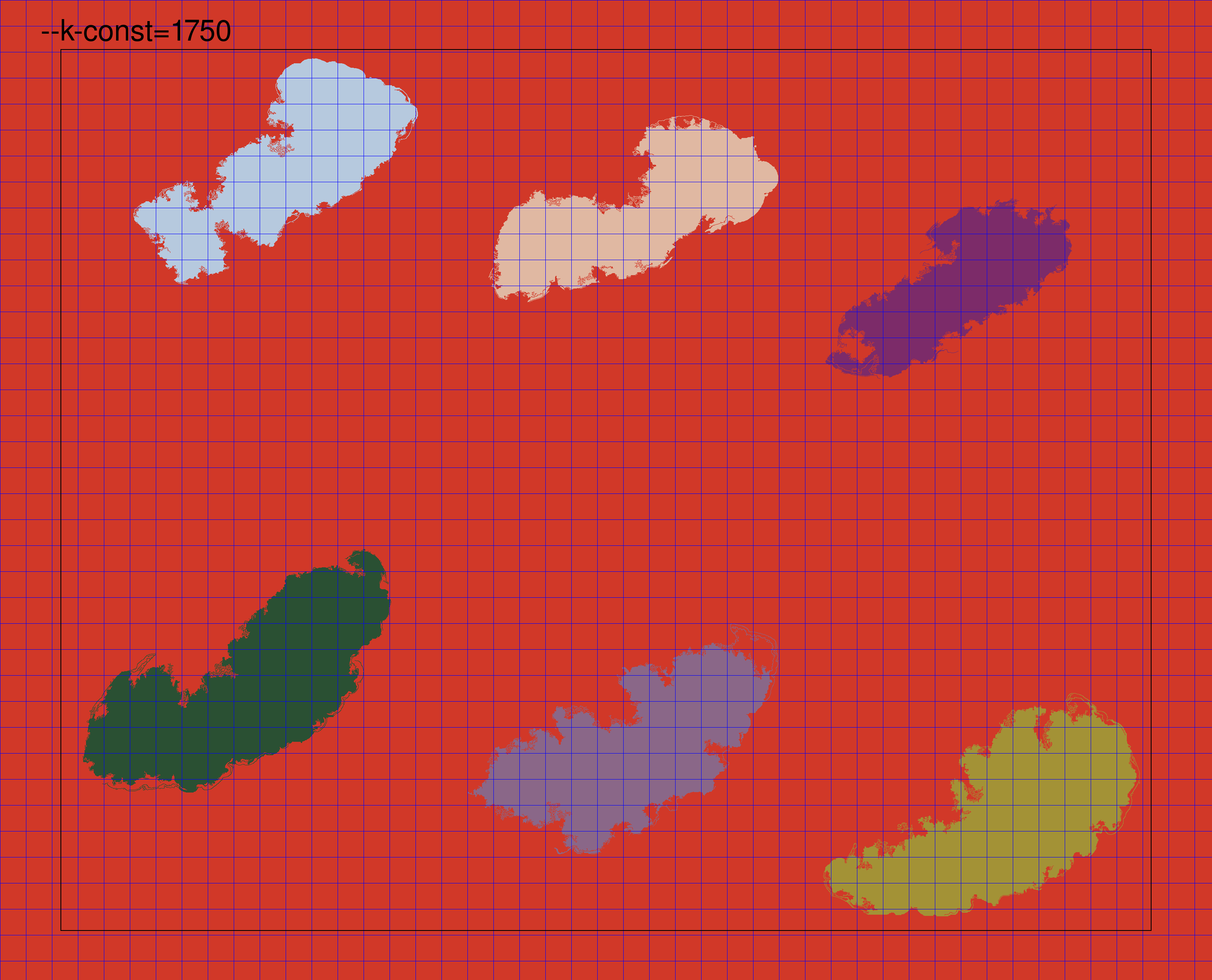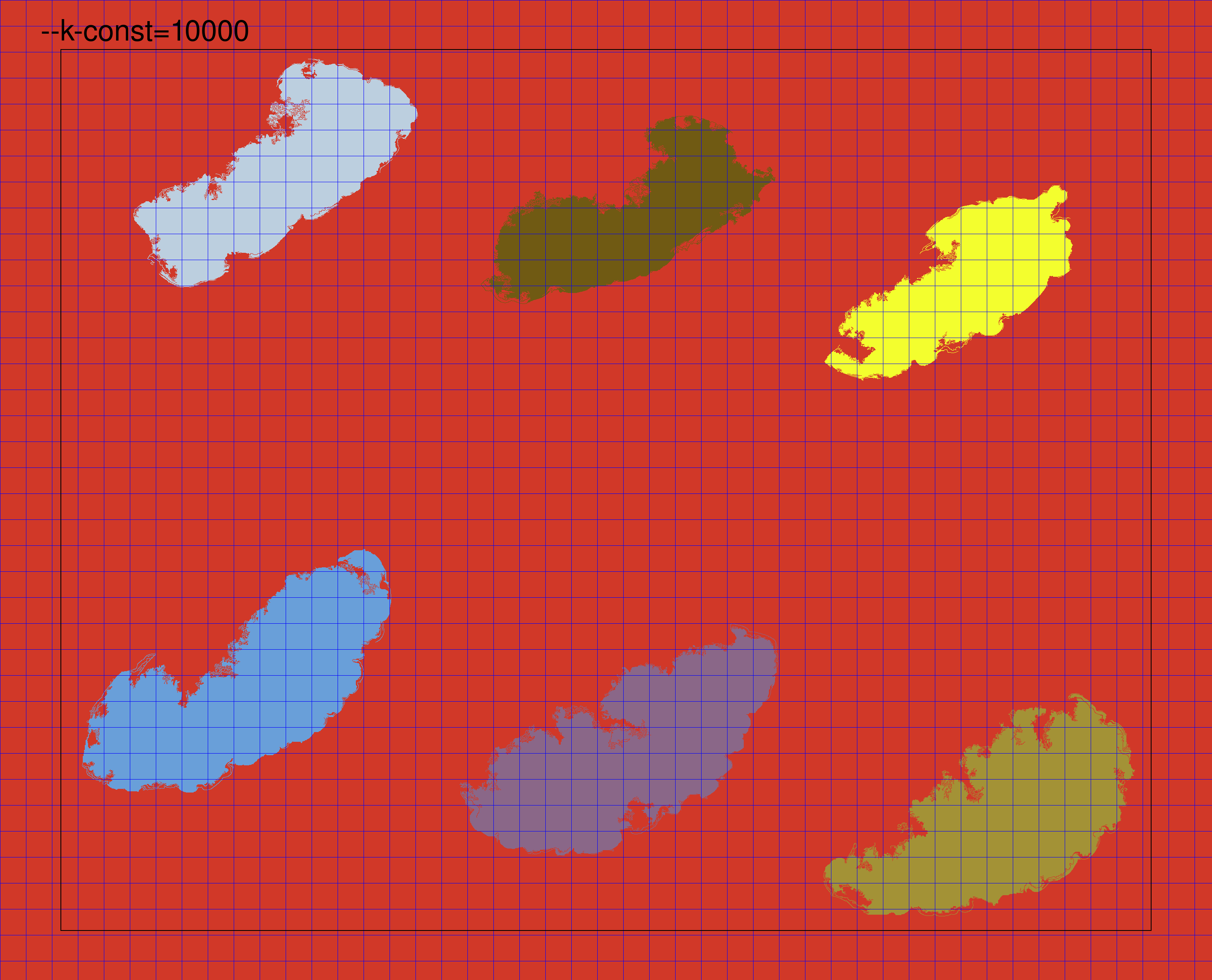
Borders and corners
In the graph-based segmentation tiling method, PyHIST identifies tissue regions and assigns a different color to each one. To perform evaluation for each tile to check if it meets the minimum foreground threshold, PyHIST needs to know what is the background color in the image. Since it is not safe to assume that the background color is the most frequent color in the image (for example, a tissue slice might cover almost all the WSI and thus, that region would be the most frequent color), PyHIST relies on either the borders and corners of the mask image to set the background color.
By default, PyHIST looks at the mask color content in the four edges (left, bottom, right, top). How much of the image border is used to determine the background is defined by the --percentage-bc argument. The number of pixels that will compose each border is simply calculated as image width x percentage-bc (left and right borders) and image height x percentage_bc (top and bottom borders). Below, we show an example of increasing the --percentage-bc in a graph test mode image. As the value increases, PyHIST uses a larger fraction of the image to evaluate the background color. The border sides that PyHIST will use to determine the background color are defined by the --borders flag. By default, PyHIST will use all the four borders to determine the background color, however, in some situations it might be desirable to use only a subset of the borders to determine the background color: for example, in a situation where there are image artifacts present in the borders (due to suboptimal tissue fixing on the slide, etc.).
 (if the lines in the animation do not show clearly, open the image in a separate window)
(if the lines in the animation do not show clearly, open the image in a separate window)
An alternative way is available in PyHIST to define the background, using the image corners to evaluate the background color in the mask image instead of the borders. The image corners (top left, bottom left, bottom right, top right) to use are controlled through the --corners flag. The size of each corner will be calculated as (image width x percentage-bc, image-height x percentage-bc). Only one of the two methods can be used at once: if the --corners flag is different from 0000, then the --borders flag must set to 0000 and viceversa.